Intensive Short Programs
Definition: deep training programs that are focused and of an applied nature, it aims to provide extensive training in one of the basic needs of the faculty members.
Duration of the program: two days (seven training hours per day), four days for "Assessment and Evaluation for Teaching and Learning" program.
Target: faculty members.
Certificates: The participant gets a certificate from DAD\IAU.
Sources of the training topics: the topics were identified after assessing and analyzing the needs of faculty members from several sources, as follows:
- Studies about the needs of the faculty members.
- Academic Leaders Surveys.
- Reports of the Quality and Academic Accreditation Deanship.
- Students’ evaluation results for the course, tutor, and for the academic program.
- Comparing and investigating global experiences in teaching and learning.
- Questionnaire of the learning facilitators (trainers).
- Recommendations of DAD Forums.
Strategies and methods that are used in training/Assessment:
- Discussion and dialog.
- Brainstorming.
- Teamwork.
- Practical applications.
- Use of technology and mobiles.
- Educational competitions.
- Related videos.
- Self-assessment/reflections and self-revision.
- Colleague's evaluation.
- Expert evaluation (trainer).
Short intensive training programs (in Arabic):
- Active learning (2 Days Program).
- Memory Engineering (2 Days Program).
- Systematic design of education and activity design (2 Days Program).
Short intensive training programs (in English):
- Designing and Implementing Effective Rubrics (2 Days Program).
- Assessment and Evaluation for Teaching and Learning (4 Days Program).
Active Learning Program
The philosophy of active learning is based on the need for active student participation during the teaching and learning process; as the student is the center of the T&L process, so the student must be active and involved in the learning activities.
Importance of the program
The importance of this program is to apply active learning strategies and skills in order to get into the core of active learning and to enhance the student's role as the center of the teaching and learning processes. On the other hand, this program integrates active learning with micro-education, by designing a simple educational situation for a specific period in terms of time and the content of the lesson and in the presence of the participants in the program, under the supervision of trainers with experience in this field.
Contents of the program
The program consists of 4 units:
Module 1: Theoretical framework.
Module 2: Educational context.
Module 3: Reflection on Active Learning Applications.
Module 4: Designing and following up on active learning tasks.
Program's objectives
- Support the vision of Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University and its mission of promoting excellence in teaching and learning in the university's academic community.
- Enhance the skills of faculty members in active learning practices relying on an organized and purposeful pedagogical method.
- Encourage faculty members to adopt strategies and methods of active learning as a classroom culture.
Learning outcomes
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
1. Demonstrates the concept of active learning.
2. Compares traditional teaching with active learning.
3. Concludes the importance of active learning.
4. Defines the roles of the teacher and the learner in active learning.
5. Demonstrates the concept of micro-teaching.
6. Determines the steps of micro-teaching.
7. Combines micro-teaching with active learning.
8. Design a typical course in his field according to the strategies and methods of active learning.
9. Implements teaching situations in his field by using active learning.
10. Proposes solutions to overcome the constraints of active learning.
Program’s Agenda
Day 1
- Concept, philosophy, and assumptions of active learning.
- Active and traditional learning, the characteristics and importance of active learning.
- Results of studies.
- Strategies and methods of active learning.
Day 2
- Micro-teaching: its concept, its importance, and its integration into active learning.
- Design educational attitudes (lectures) in accordance with active learning strategies.
- Implement educational attitudes in accordance with the integration of active learning with micro-teaching.
Memory Engineering Program: "Employing recollecting aids in the educational process"
This program will cover the theoretical and practical aspects of the information processing system model, one of the cognitive theories that is a scientific revolution in memory study and human learning processes, where it has tried to clarify and explain the mechanism of occurrence of these processes and their role in the information processing and the production of behavior.
Importance of the program
The importance of the program is to enable faculty members to improve student learning by integrating students with activities and applications that increase their attention and help them receive, process and then easily retrieve information when needed, and using practical applications that will contribute to improving Recalls such as; Mental Maps/ places/ first letters, stories...Etc.
Contents of the program
The program consists of 6 scientific units:
Module 1: An introduction to the nature of the brain, the human mind and the information processing system.
Module 2: The Educational Context of the Information Processing System/Research Results.
Module 3: Memory types.
Module 4: Basic processes in the information processing system.
Module 5: Oblivion and Remembrance.
Module 6: Practical applications in recollection aids.
Program objectives
1. Support the vision of Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University and its mission of promoting excellence in teaching and learning in the university's academic community.
2. Highlight the role of faculty members in improving student learning using recollection aids.
3. Provide the participant with the knowledge, skills and positive attitudes towards the employment of remembering aids in the classroom.
4. Enhance students' learning by integrating them with activities and applications that increase their attention and help them receive information, store it and then retrieve it when needed.
Learning outcomes for the training program
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
- Conclude the definition of the information processing system is.
- Determines the expected roles of faculty members towards students based on the types and characteristics of memory.
- Concludes the role of the faculty member in assisting students in each information processing process.
- Uses remembering aids in the educational process.
Program’s Agenda
Day 1
- Brain memory story.
- Human mind and computer.
- Information processing model assumptions.
- Results of research in the information processing system.
- Memory types.
- Basic processes in the information processing system.
Day 2
- Forgetfulness and remembrance
- Practical applications in the following remembering aids:
1. Replacement of places.
2. Initials.
3. Keywords.
4. SRKW Strategy in Summary.
5. Meditation.
6. Re-learning and review.
7. Anecdotal Synthesis.
8. Chain Method.
9. Cornell's Way to Take Notes.
10. Mental Maps.
Systematic design of education and activities
The design of teaching systems is a process that aims to verify that learning is not done by chance or randomly, but teaching is built according to a process with specific outcomes. This program will cover the stages of curriculum design and the design of activities that lead to greater achievement in the learning process.
Importance of the program
The importance of the program is to enable faculty members to improve student learning, through the systematic design of materials, enhanced by the prior planning of activities and applications that will engage students in the learning process and make them a center of it.
Contents of the program
The program consists of 5 scientific units:
Module 1: Systematic Design of Education "Dick and Carey Model".
Module 2: Designing educational activities " ARCS model".
Module 3: Systematic Design of Education "Dick and Carey Model"/Applications.
Module 4: Designing Educational Activities "ARCS Model"/ Applications.
Module 5: Rubric design for the activities/ Practical applications.
Program objectives
- Support the vision of Imam Abdul Rahman bin Faisal University and its mission of promoting excellence in teaching and learning in the university's academic community.
- Raising the efficiency of the educational process by preparing the systematic and elaborate design of the subjects.
- Enhance the student's role in the educational process by pre-planning activities.
- Enhance the competence and skill of the faculty member to apply the systematic design.
Learning outcomes for the training program
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
- Design an academic course using the "Dick and Carey" model.
- Design the course that includes the motivational strategies of learning.
- Applies the Keller model; the design of the stimulus approach ARCS model.
- Applies strategies to enhance student participation in the classroom.
- Prepare a Rubric for the student’s participation in and out of the classroom.
Program’s Agenda
Day 1
- Systematic design of education (Dick and Carey model).
- Designing educational coerces; comparison between the past and the present.
- Objectives and advantages of the systematic design of education.
- Explain the steps of the Dick and Carrie model.
- Promoting student participation through motivational design (ARCS model).
- The impact of enhancing student participation on academic achievement.
- Strategies to promote the participation of learners.
- Arcs motivational Model.
- Student’s participation Rubric.
Day 2
- Review and discuss the topics of the first day.
- Practical application of participants’ design of one topic with its activities.
- Participants' presentations and feedback.
Short intensive training programs (in English)
- Designing and Implementing Effective Rubrics (2 Days Program).
- Assessment and Evaluation for Teaching and Learning (4 Days Program).
Designing and Implementing Effective Rubrics
In essence, rubrics are a labeling instrument that lists project specifications, contracts, or other work elements. List the rubrics for a certain score or grade. This allows the student to develop his / her job before applying. Teachers need to clarify the grades of the rubric.
Importance of the program
Interpretation of student expectations, performance development, simultaneous student input and planning, timely and comprehensive reviews, contact with colleagues and practice enhancement.
Contents of the program
The program consists of 5 scientific units:
Module 1: Define Rubric, Purpose, & Usage of Rubric.
Module 2: Describe the Benefits of Rubrics & Misconceptions.
Module 3: Rubric structure, Types & Levels of Performance.
Module 4: Module 4: Identifying Rubric parts and steps.
Module 5: How to Create a Rubric?
Module 6: develop grading Rubrics and evaluation.
Program objectives
- Communicating what is expected of a given performance or product before it takes place to teachers and students.
- Evaluate the quality of the performance or output until finished.
Learning outcomes for the training program
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
- Identifying Rubrics components and steps.
- Identify origin, purposes and uses of Rubric.
- Explain benefits and misunderstandings.
- Evaluate and build rubrics.
Program’s Agenda
Day 1
- Define Rubric, Purpose, & Use of Rubric.
- Describe Benefits & Misconceptions.
- Rubrics structure, Types & Levels of Performance.
Day 2
- Identifying Rubric parts and steps?
- How to Create a Rubric.
- How to develop grading Rubrics.
- Procedure for creating evaluation Rubrics.
Assessment and Evaluation for Teaching and Learning
The concerns of and need for assessment in higher education have increased to the highest level due to the challenges of teaching and learning assessment. Thus, an intensive training program that was developed based on the best practices in the field of teaching assessment and instructor development.
Importance of the program
The lack of consistent assessment tools to measure instructors' teaching skills and students' learning justifies an intensive assessment of teaching and learning programs.
Contents of the program
The program consists of 5 scientific units:
Module 1: Introduction to Assessment in Higher Education.
Module 2: Providing Constructive Feedback.
Module 3: Learning Outcomes for Programs & Courses.
Module 4: Preparing a Test on Blueprint.
Module 5: Questioning to Develop HOT.
Module 6: Constructing and Conducting Assessment Tools.
Module 7: High-Quality Assessment through Rubrics.
Module 8: Effective Formative Assessment for the Classroom.
Module 9: Improving Faculty Grading Practices.
Module 10: Assessing Projects and Labs.
Module11: Analyzing Test Items.
Program objectives
- To enhance the excellence in teaching and learning through the excellence in applying assessment and evaluation.
- To advance faculty knowledge and skills on key concepts and methods of assessment and evaluation.
- To improve the competencies of faculty members concerning the implementation of non-traditional, alternative and performance-based assessment and evaluation.
- To improve instructors' decision-making skills in relation to assessment and evaluation.
Learning outcomes for the training program
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
- Explain key principles, concepts and methods in relation to assessment and evaluation in higher education.
- Identify appropriate and relevant assessment tools that address the different levels of cognitive learning skills, especially higher-order-thinking skills, and the different learning outcomes.
- Discuss alternative assessment and evaluation methods.
- Create a strong relationship between instruction and assessment in the classroom.
- Develop non-traditional assessment tools appropriate for students' learning progress.
- Apply various methods for providing constructive feedback to students.
- Analyze student learning and make relevant inferences utilizing evidence-based assessment in the classroom.
- Plan for the development of students’ skills to practice self- and peer- assessment strategies.
- Adopt to sharing their assessment and evaluation practices in the classroom with colleagues and the wider academic community.
Program Agenda
Day 1
- Introduction to Assessment in Higher Education.
- Providing Constructive Feedback.
- Learning Outcomes for Programs & Courses.
Day 2
- Preparing a Test on Blueprint.
- Questioning to Develop HOT.
- Constructing and Conducting Assessment Tools.
Day 3
- High-Quality Assessment through Rubrics.
- Effective Formative Assessment for the Classroom.
- Improving Faculty Grading Practices.
Day 4
- Assessing Projects and Labs.
- Analyzing Test Items.
This training program intended to cover The Assessment Cycle from A-Z:
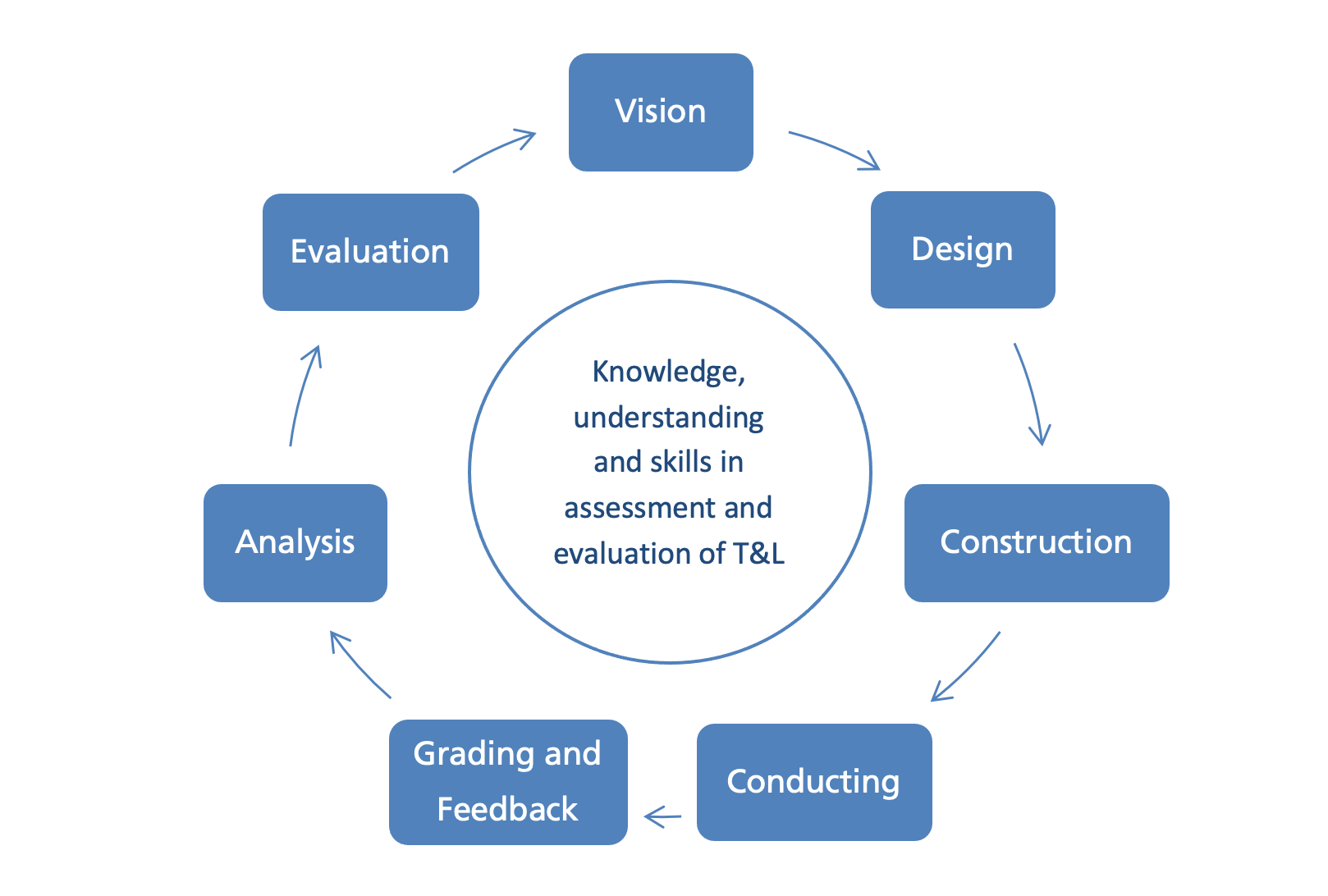
Duration: 4 days, Total of 20 hours.
Venue: Deanship of Academic Development (D27), Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University, Dammam, Saudi Arabia.
Target: faculty members.
Certificates: The participant gets a certificate from DAD\IAU.
Assessment and Evaluation for Teaching and Learning in Higher Education
Contents of the program
The program consists of 5 scientific units:
Module 1: Introduction to Assessment in Higher Education.
Module 2: Effective formative Assessment for the Classroom.
Module 3: Prepare a Test Based on Blueprint.
Module 4: Assessing Projects and Labs.
Module 5: Constructive Feedback.
Module 6: Developing Multiple-Choice Questions.
Module 7: High-Quality-Assessment through Rubric.
Module 8: Questioning to Develop HOT Skills.
Module 9: Constructing Advanced Multiple-Choice Questions.
Module 10: Improving Faculty Grading Practices.
Module11: Analyzing Test Items.
Program objectives
- To enhance the excellence in teaching and learning through the excellence in applying assessment and evaluation.
- To advance faculty knowledge and skills on key concepts and methods of assessment and evaluation.
- To improve the competencies of faculty members concerning the implementation of non-traditional, alternative and performance-based assessment and evaluation.
- To improve instructors' decision-making skills in relation to assessment and evaluation.
Learning outcomes for the training program
At the end of this program, the participant will be able to:
- Explain key principles, concepts and methods in relation to assessment and evaluation in higher education.
- Identify appropriate and relevant assessment tools that address the different levels of cognitive learning skills, especially higher-order-thinking skills, and the different learning outcomes.
- Discuss alternative assessment and evaluation methods.
- Create a strong relationship between instruction and assessment in the classroom.
- Develop non-traditional assessment tools appropriate for students' learning progress.
- Apply various methods for providing constructive feedback to students.
- Analyze student learning and make relevant inferences utilizing evidence-based assessment in the classroom.
- Plan for the development of students' skills to practice self-and peer-assessment strategies.
- Adopt to sharing their assessment and evaluation practices in the classroom with colleagues and the wider academic community.
Program Agenda
Day 1
- Explore the background history of assessment in higher education.
- Discuss the concept, purposes, and goals of assessment.
- Describe validity and reliability fairness.
Day 2
- Define formative assessment and its characteristics.
- Apply effective formative assessment techniques in the classroom.
- Measure immediate assessment techniques in the classroom.
- Explain teaching and learning through classroom Assessment Techniques.
Day 3
- Consider assessment at the beginning of the course.
- Ensure the validity of tests.
- Use a blueprint to prepare a test.
Day 4
- Define 21st C skills in the context of higher education.
- Explain the importance of Assessment.
- Understand project-based learning and assessment.
- Comprehend laboratory-based learning and assessment.
Day 5
- Explain the concept, objectives, and importance of feedback.
- Discuss the characteristics and benefits of constructive Feedback.
- Distinguish between effective feedback and other responses.
- Assess the effectiveness of feedback for learning.
Day 6
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of multiple-choice items.
- Use terms and analyze MC items.
- Construct items that address the different levels of cognitive learning skills، especially HOTS.
- Review examples of effective and ineffective MC items.
Day 7
- Define rubrics and explain the characteristics of high-quality assessment.
- Distinguish between rubric types (formats).
- Identify rubric components.
- Explain the importance of using rubrics for high-quality assessment.
- Create a stand-alone rubric.
Day 8
- Define the concept of questioning.
- Recognize the importance of Bloom's taxonomy as a taxonomy of questions.
- Identify the characteristics of questioning.
- Basics of asking questions.
- Write questions to cover HOTS.
Day 9
- Construct Multiple-Choice Questions Test HOTs.
- Use extended Matching Questions Higher-Order-Thinking.
- Apply modified Essay Questions Higher-Order-Thinking.
- Practice effective and ineffective MEQs and EMQs.
Day 10
- Discuss the purpose and challenges of grading.
- Explain the importance of efficient grading for student learning.
- Select appropriate grading practices for student learning.
- Evaluate their own grading practices in light of effective grading guidelines.
- Make an argument for applying an ongoing process to improve their practices of grading.
Day 11
- Understand and use a normal distribution graph for scores' interpretation.
- Identify and apply the Z-scores formula to interpret scores.
- Find and calculate the percentile ranks for each particular score.
- Compute and analyze item statistics such as difficulty, discrimination, and quality for sake of improvement.

